Dbs101_unit1
Topic : Database Systems Fundamentals
Lesson 1:
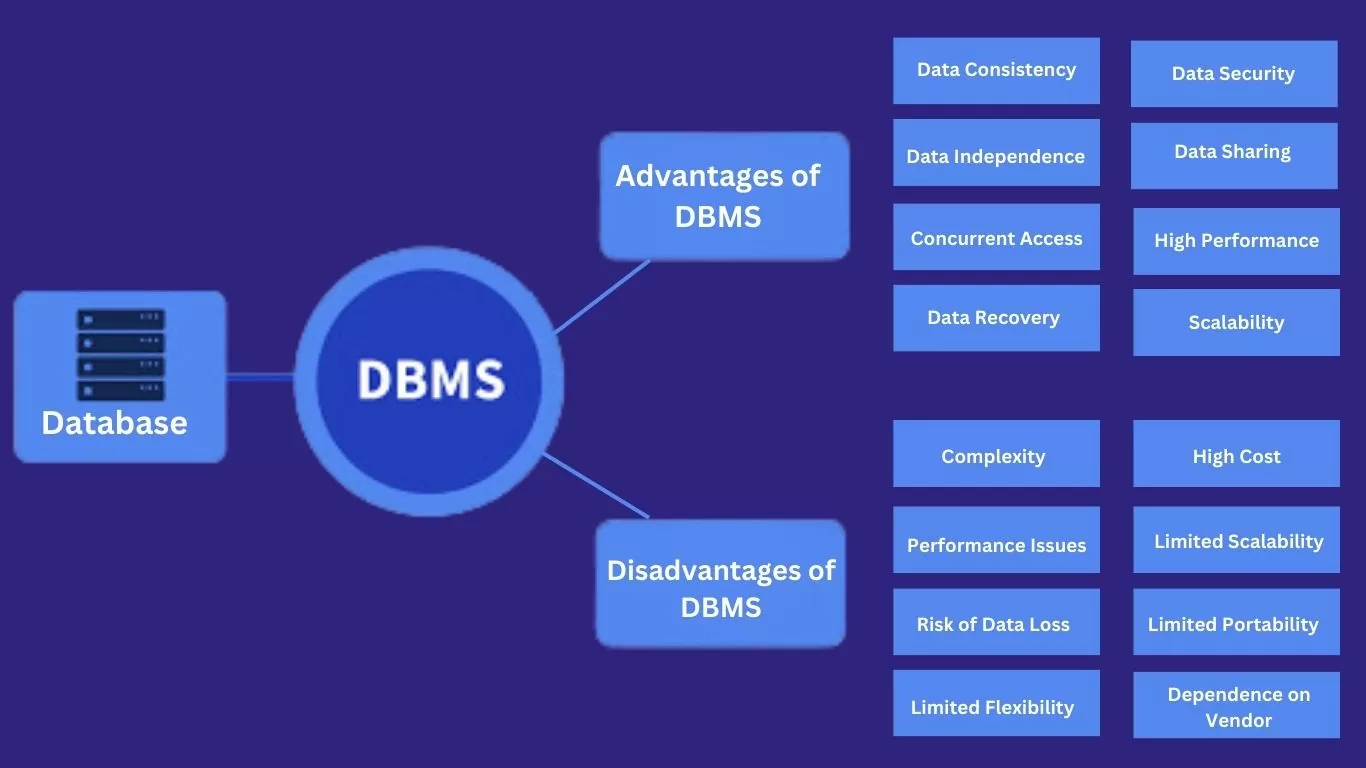
Key Points from the Unit – Databases: Organized collections of electronically stored data.
- Database Management System (DBMS): Software that allows efficient data storage, retrieval, and manipulation.
- Advantages of DBMS:
- Ensures data consistency
- Scalable and secure
- Reduces redundancy
- Improves data organization
- Disadvantages of File-Processing Systems:
- Data redundancy
- Difficult data retrieval
- Integrity issues
- Security risks
- Importance of DBMS:
My Learning and Importance
Learning Database Systems is Important: Data has now become the most important asset in the world where digital is prevailing. The study of databases provides a good grounding onto modern database management systems from inefficient file-based systems.
Core Benefits of Databases: Applications become trustworthy, accessible, and secure for all users. They increase the efficiency and reliability of real-world systems.
Personal Growth and Reflection
- What I Learned:
- Improved critical thinking and problem-solving about how databases help manage data better.
- Learned how database systems make applications more efficient.
- Why It Matters:
- Organizing data properly improves productivity, decision-making, and services.
Lesson 2:
Lessons in the database systems fundamentals include the following:
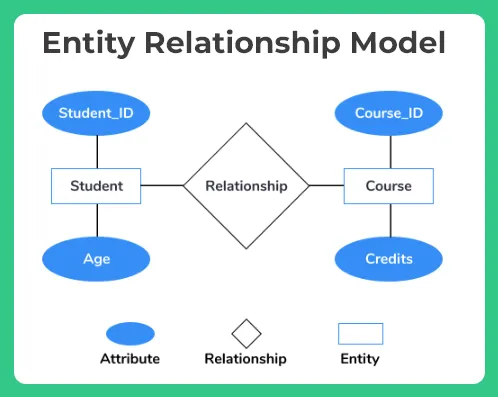
1. Understanding Data Models
- The data models define the shape and form in which data resides in a database.
- The four main data models cover:
- Entity-Relationship Model
- Semi-Structured Data Model
- Object-Based Data Model
- Relational Model
- This entails the designing of efficient databases that allow specification of appropriate use.
2. Database Languages and Their Applications
- SQL (Structured Query Language) is a basis on which database is established and interacted with.
- Two major groups of these languages are:
- DDL(Data Definition Language): Defines schema and constraints.
- DML (Data Manipulation Language): Accesses, inserts, deletes, or updates the data.
- SQL supports both data manipulation approaches, declarative and procedural.
3. Database Architecture and Components
- The multi-layered abstraction system of database architecture includes:
- Physical Level: How data is stored.
- Logical Level: What data is stored and how it relates to each other.
- View Level: Defined simplified view of the database to users.
- It is composed of the following components:
- Storage Manager
- Query Processor
- Transaction Management
- Each of these elements gives a critical foundation to the efficient management and optimization of databases.
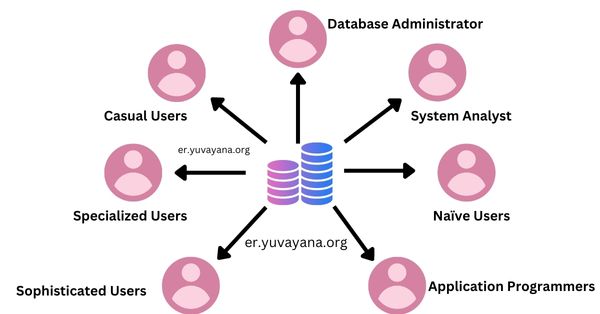
4. Types of Database Users and Roles
- Database Users:
- End Users: Users who invoke applications to get data or update it.
- Application Developers: Application development for the database to be utilized.
- Database Administrators (DBAs): tasked with maintenance of integrity, security, and performance of the database.
- System Analysts and System Designers: defines the database structure and functionalities.
- The DBA works towards ensuring that the database system runs appropriately.
5. Importance of Database Design
- Database design process includes blueprinting:
- Suitable data model selection.
- Conceptual design to pin down on functional requirements.
- Logical design-for schema mapping to a database system.
- Physical design-for storage and performance aspects.
- An efficient database gets rid of redundancy in designing a designed database and thus improves data integrity.
What I Learned
– Learning different data models helps design efficient data storage and management systems.
- SQL is essential for querying data, a key skill in software development and analytics.
- Understanding database architecture and user roles ensures secure and effective database administration.
Reasons that make this important-
Understanding database architecture and user roles is necessary for managing databases and thus their security.
Personal Growth and Reflection
- Improved my analytical thinking by learning how to organize data for easy retrieval.